2020年7月31日,张波及其合作者在计算力学顶级期刊《International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering》上发表题为“Strain gradient differential quadrature finite element for moderately thick micro-plates”的研究成果。
当材料或结构的特征尺寸减小至微米乃至亚微米量级时,其力学特性将呈现出显著的尺度依赖性,经典连续介质力学及与之相关的传统实验方法难以刻画此类现象。研究者发现尺度效应是由材料或结构的空间离散特性而导致面内变形的约束限制不同引起的。事实上,当梁、板、壳等结构的特征尺寸与其组分材料的内禀长度处于同一量级或者比较接近时,尺度效应的影响将不可忽略。为了描述微构件的尺度效应,人们发展了若干种非经典连续介质力学理论,如应变梯度理论、偶应力理论、非局部理论等,并将之应用于微尺度结构力学问题的建模与分析中。在偶应力/应变梯度理论中,高阶位移梯度项的引入使得微尺度结构力学模型的控制方程阶次显著增加,从而导致位移场的高阶连续性要求,这给各类边值问题的分析求解带来了极大困难。目前, 人们主要借助于高阶弱连续有限元、等几何分析以及微分求积等方法求解高阶微尺度梁、板、壳的静动力学问题。
张波及其合作者汲取了标准有限元法在施加边界条件以及对复杂几何形状的适应性等优点和微分求积法在实现高阶位移场连续性方面的优点,通过构造了四阶和六阶微分求积几何映射策略,实现了偶应力/应变梯度理论框架下微尺度结构力学问题中位移场的C1和C2连续性要求。采用势能泛函对微尺度结构边值问题进行弱形式描述,借助于微分求积准则将单元势能泛函离散为Gauss-Lobatto求积点处位移参数的函数,利用微分求积几何映射策略将求积点处位移参数转换为结点处位移参数,最后由最小势能原理导出单元方程。以应变梯度梁及板结构为研究对象,分别构造了应变梯度Euler-Bernoulli梁单元、Timoshenko梁单元、Reddy梁单元、C2部分连续的Kirchhoff板单元、C2连续的Kirchhoff板单元以及无剪切锁死的C1连续四边形Mindlin–Reissner板单元等,以上单元类型均属于首次报道。通过将标准有限元法的缩减总刚度(或质量)矩阵的1-范数和作者提出梯度型微分求积有限元法(退化为宏观尺度的情形)的缩减总刚度(或质量)矩阵的1-范数进行对比,结果表明前者明显大于后者,表明了作者所提出方法对应的缩减总刚度(或质量)矩阵更加良态,从而阐明了微分求积有限元法收敛性优势的内在原因。
对于应变梯度微分求积Mindlin–Reissner四边形板单元,构造如下微分求积几何映射
策略来实现挠度函数和转角函数的C1连续性要求:
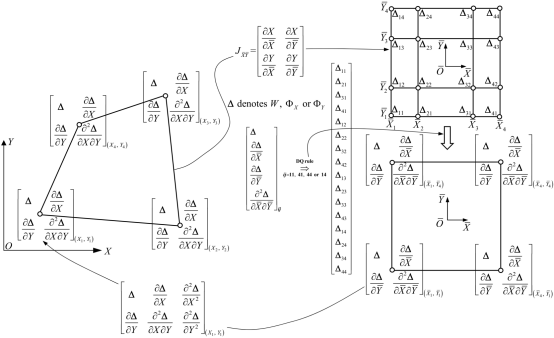
微分求积几何映射策略示意图
构造增强型分片检验函数如下:
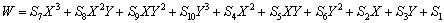
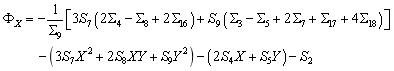
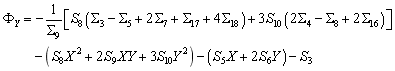
其中
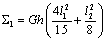 ,
, 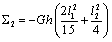 ,
, 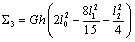 ,
,
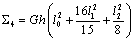 ,
, 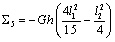 ,
, 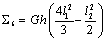 ,
, 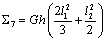 ,
,
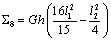 ,
, 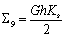 ,
, 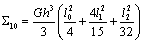 ,
, 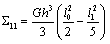 ,
,
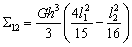 ,
, 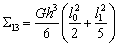 ,
, 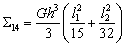 ,
, 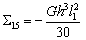 ,
,
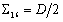 ,
, 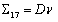 ,
, 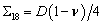 ,
, 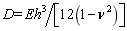
分片网格如下:

分片检验示意图
分片试验的节点位移响应:
节点 |
节点参数 |
|
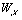
|
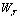
|
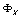
|
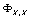
|
|
|

|
|
(0.4, 0.2) |
0.4608(a) |
1.1200 |
1.1320 |
-1.1955 |
-2.8000 |
-1.5000 |
-1.2276 |
-1.5000 |
-3.1200 |
0.4608(2) |
1.1200 |
1.1320 |
-1.1955 |
-2.8000 |
-1.5000 |
-1.2276 |
-1.5000 |
-3.1200 |
(1.8, 0.3) |
7.2028(a) |
9.5390 |
5.3940 |
-9.6145 |
-8.8400 |
-3.9200 |
-5.4896 |
-3.9200 |
-6.2400 |
7.2028(b) |
9.5390 |
5.3940 |
-9.6145 |
-8.8400 |
-3.9200 |
-5.4896 |
-3.9200 |
-6.2400 |
(1.6, 0.8) |
8.6472(a) |
9.8800 |
8.3320 |
-9.9555 |
-8.8000 |
-4.5000 |
-8.4276 |
-4.5000 |
-8.8800 |
8.6472(b) |
9.8800 |
8.3320 |
-9.9555 |
-8.8000 |
-4.5000 |
-8.4276 |
-4.5000 |
-8.8800 |
(0.8, 0.8) |
3.2008(a) |
4.1840 |
5.2440 |
-4.2595 |
-5.4400 |
-3.2200 |
-5.3396 |
-3.2200 |
-7.4400 |
3.2008(b) |
4.1840 |
5.2440 |
-4.2595 |
-5.4400 |
-3.2200 |
-5.3396 |
-3.2200 |
-7.4400 |
(a) 精确; (b) 数值
采用应变梯度微分求积Mindlin板单元研究如下环状扇形微板和实心椭圆微板:
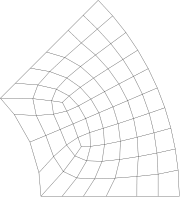
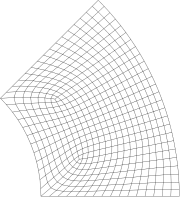
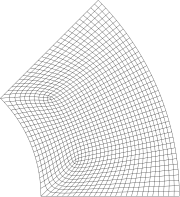
I: 86个节点, 72 个单元 II: 536 个节点,500 个单元 III: 1297 个节点1240 个单元
环状扇形微板的三种网格
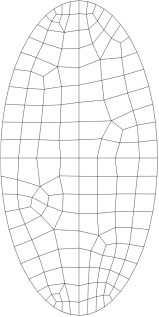
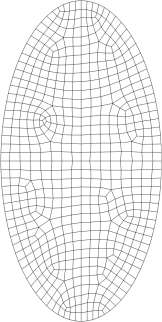
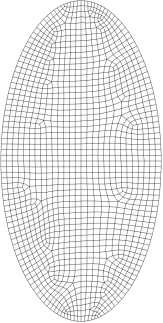
I: 178 个节点,151 个单元 II:630 个节点,581 个单元 III: 1449 个节点,1372个单元
实心椭圆微板的三种网格
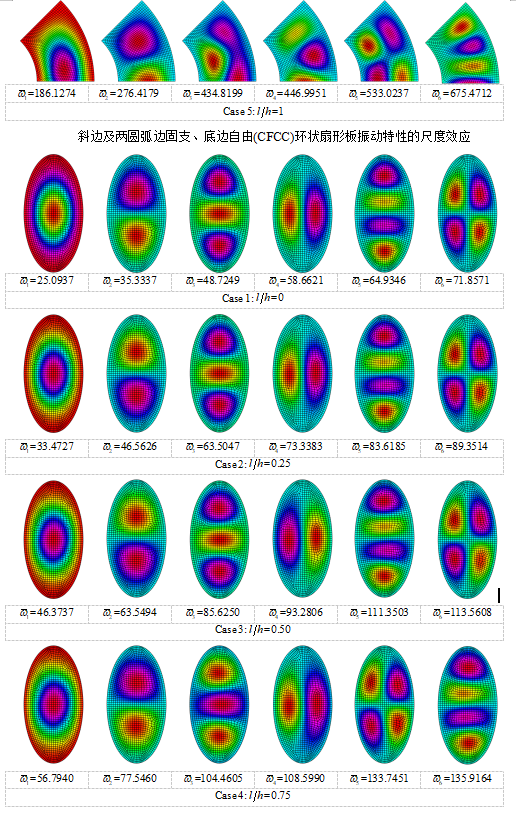
微分求积有限元法预测的四边固支环状扇形板的前6阶振动频率及模态如下:
微分求积有限元法预测的四边简支环状扇形板的前6阶振动频率及模态:
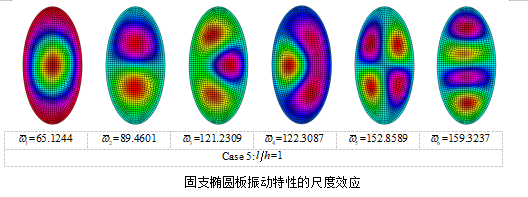
本文单元所预测的固支椭圆板的前6阶振动频率及模态如下:
本文单元所预测的简支椭圆板的前6阶振动频率及模态如下:
本文单元与著名的Bogner-Fox-Schmidt (BFS)四边形板单元(C1连续)所对应缩减刚度(或质量)矩阵条件数的对数比较:
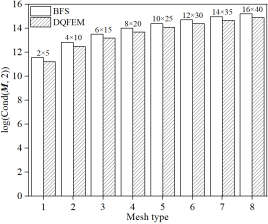
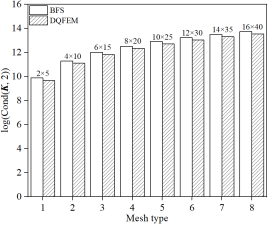
(a) 缩减质量矩阵 (b) 缩减刚度矩阵
四边简支中厚板
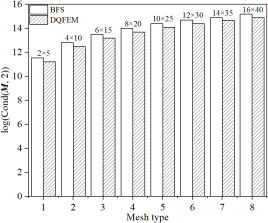
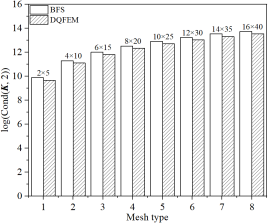
(a) 缩减质量矩阵 (b) 缩减刚度矩阵
四边固支中厚板
微尺度中厚环状扇形板和椭圆板振动频率及模态的尺度效应:

应变梯度微分求积有限元法的相关著作:
[1] B. Zhang, H. Li, L. Kong, X. Zhang, Z. Feng. Strain gradient differential quadrature finite element for moderately thick micro-plates. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2020 DOI: 10.1002/nme.6513. (47 pages)
[2] B. Zhang, H. Li, L. Kong, J. Wang, H. Shen. Strain gradient differential quadrature beam finite elements. Computers & Structures 218 (2019) 170-189. (20 pages)
[3] B. Zhang, H. Li, L. Kong, X. Zhang, H. Shen. Strain gradient differential quadrature Kirchhoff plate finite element with the C2-partial compatibility, European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids (2020) 103879. (27 pages)
[4] B. Zhang, H. Li, L. Kong, H. Shen, X. Zhang. Size-dependent vibration and stability of moderately thick functionally graded micro-plates using a differential quadrature-based geometric mapping scheme, Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements 108 (2019) 339-365. (27 pages)
[5] B. Zhang, H. Li, L. Kong, H. Shen, X. Zhang. Size-dependent static and dynamic analysis of Reddy-type micro-beams by strain gradient differential quadrature finite element method, Thin-Walled Structures (2020) 106496. (26 pages)
[6] B. Zhang, H. Li, L. Kong, H. Shen, X. Zhang. Coupling effects of surface energy, strain gradient, and inertia gradient on the vibration behavior of small-scale beams. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences (2020) 105834. (21 pages)
[7] B. Zhang, H. Li, J. Liu, H. Shen, X. Zhang. Surface energy-enriched gradient elastic Kirchhoff plate model and a novel weak-form solution scheme. European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids, 2020. (33 pages).
[8] Bo Zhang, H. Li a, L. Kong, X. Zhang, Z. Feng. Variational formulation and differential quadrature finite element for freely vibrating strain gradient Kirchhoff plates. ZAMM-Zeitschrift fuer Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 2020.
[9] Bo Zhang, H. Li a, L. Kong, X. Zhang, Z. Feng. Weak form differential quadrature finite element formulations for functionally graded micro-beams with strain gradient effects. Acta Mechanica, 2020.
该研究受到香港理工大学建筑与房地产学系李恒教授主持的“Digital Construction and Smart Construction Technologies”研究项目的资助。该项成果完成人包括张波、李恒教授、孔刘林博士(地质大学)、沈火明教授以及张旭教授。



